Stay up to date.
Stay connected with tips, resources & stories on language access.

For healthcare consumers, the expected cost, quality and outcome of their care can be daunting. This is even more complicated for patients at the highest risk of not getting the care they need – especially those with limited-English proficiency (LEP). To help bridge the gap, CMS uses a star rating system to compare safety, quality and patient satisfaction.
 The Importance of CMS Star Ratings
The Importance of CMS Star RatingsIn 2015, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) unveiled a star rating system to objectively measure patient satisfaction, safety and healthcare quality in hospitals.
These ratings improve transparency to help patients find the facilities with the highest quality care and patient satisfaction scores. Payers (including CMS and commercial payers) also use star ratings to financially reward facilities that score well and penalize those that fall short. For example, lower ratings can incur financial penalties and lower Medicare reimbursement rates.
For hospitals, improving CMS star ratings begins with understanding what metrics are included in the calculations. Overall star ratings are based on objective data related to specific patient outcomes. CMS tracks more than 100 metrics in five categories, including safety, patient experience and readmission rates.
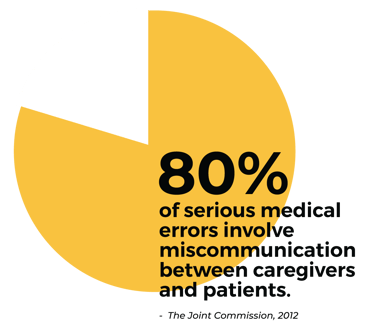
Communication errors are one of the primary causes of medical errors in hospitals. LEP patients are at the highest risk of communication errors that could lead to serious harm. The population of LEP patients in the U.S. is large and growing – more than 25 million people do not speak English well enough to understand information in a hospital or critical care setting. Improving access to language support is an effective way to alleviate communication errors and improve CMS ratings.
Download our free whitepaper to learn more about how language support can improve your hospital’s CMS star rating: